HCG Treatment Decision Tool
Choose Your Treatment Scenario
Answer these questions to get a personalized recommendation based on your specific needs.
Recommended Option
Comparison of Options
Looking for a clear picture of how ZyhCG stacks up against other HCG products and non‑HCG options? This guide breaks down the science, the price points, the safety profile, and the real‑world outcomes so you can decide whether ZyhCG is the right fit for your weight‑loss or fertility goals.
Key Takeaways
- ZyhCG is a prescription‑grade HCG injection with a 26‑IU per vial strength, designed for short‑term weight‑loss protocols and assisted‑reproductive cycles.
- Major rivals - Pregnyl, Novarel, and Ovidrel - differ mainly in dosage form, FDA‑approval status, and cost per IU.
- Non‑HCG alternatives (low‑calorie diet, exercise, metformin, clomiphene) target the same outcomes via different mechanisms and may be safer for long‑term use.
- Choosing the right product hinges on three factors: treatment goal (weight loss vs fertility), duration of therapy, and budget.
- All HCG products carry similar side‑effects; monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential.
What Is ZyhCG?
ZyhCG is a pharmaceutical preparation of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) used under medical supervision for weight‑loss protocols and for supporting the luteal phase in assisted reproduction. It is supplied in 5ml vials, each containing 130IU of HCG, and is marketed primarily in Australia and New Zealand.
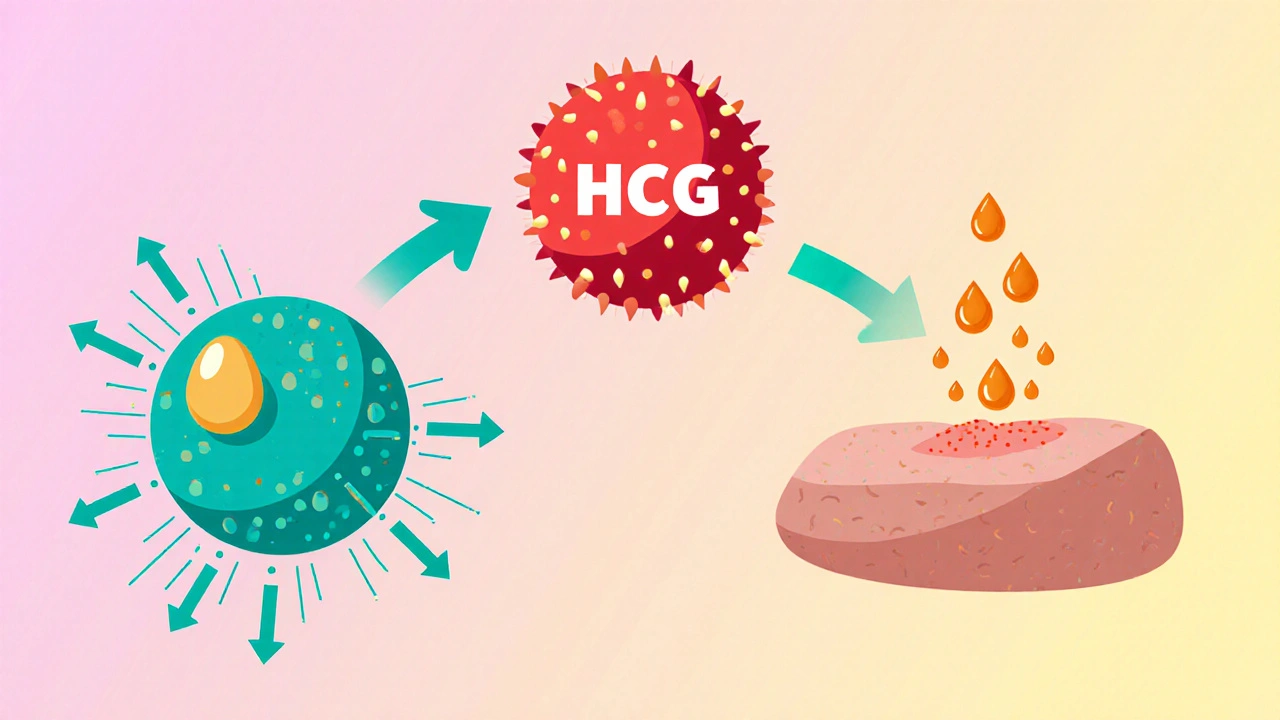
How Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Works
HCG mimics the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge that naturally occurs in the menstrual cycle. In fertility treatments it triggers ovulation, while in weight‑loss regimens it is thought to mobilize stored fat by increasing lipolysis, although the evidence is mixed. The hormone binds to LH receptors on ovarian theca cells and on adipocytes, activating the cAMP pathway that releases testosterone and free fatty acids.
Major HCG Alternatives on the Market
Below are the most common prescription‑grade HCG products that clinicians prescribe alongside or instead of ZyhCG.
- Pregnyl - a 75‑IU/mL solution produced by Merck, approved for both fertility and weight‑loss indications.
- Novarel - a 100‑IU/mL preparation from Ferring, often used in IVF cycles due to its higher concentration.
- Ovidrel - a recombinant HCG (rHCG) at 250µg per dose, primarily intended for triggering ovulation.
For patients who prefer to avoid injections, several non‑HCG options address the same goals.
- Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) - oral selective estrogen receptor modulator that stimulates endogenous LH surge.
- Letrozole - aromatase inhibitor used off‑label for ovulation induction.
- Metformin - insulin‑sensitizer often prescribed for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and can aid weight loss.
- Low‑calorie diet + exercise regimen - the backbone of any sustainable weight‑loss program.
Comparison Table: ZyhCG vs Prescription HCG Brands vs Non‑HCG Options
| Product | Formulation | IU per ml | Typical Use | Cost (USD per IU) | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZyhCG | Purified HCG powder reconstituted with sterile water | 26IU/ml | Weight‑loss protocols, luteal support | ~0.08 | Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)‑approved in NZ/AU |
| Pregnyl | HCG lyophilized powder | 75IU/ml | Fertility cycles, weight loss | ~0.10 | FDA‑approved, EMA‑registered |
| Novarel | HCG solution | 100IU/ml | IVF luteal phase support | ~0.12 | FDA‑approved |
| Ovidrel | Recombinant HCG (rHCG) | 250µg (≈6IU) per pre‑filled syringe | Ovulation trigger | ~0.15 | FDA‑approved |
| Clomiphene (Clomid) | Oral tablets | - | Ovulation induction | ~0.02 per 50mg | FDA‑approved |
| Letrozole | Oral tablets | - | Ovulation induction (off‑label) | ~0.03 per 2.5mg | FDA‑approved |
| Metformin | Oral tablets | - | Weight management in PCOS, insulin sensitization | ~0.01 per 500mg | FDA‑approved |
Decision Framework: When to Pick ZyhCG Over the Rest
Use the following three‑step checklist to match your clinical goal with the most suitable product.
- Define the primary outcome. If you need a short‑term, medically supervised weight‑loss boost, an injectable HCG (ZyhCG, Pregnyl, Novarel) is appropriate. For pure ovulation induction, recombinant options (Ovidrel) or oral agents (Clomid, Letrozole) may be cheaper and easier.
- Assess treatment duration. ZyhCG is typically prescribed for 2‑4weeks. Longer cycles (>6weeks) increase the risk of antibody formation; non‑HCG alternatives become preferable.
- Consider cost and accessibility. In NewZealand, ZyhCG often costs less per IU than imported brands. However, insurance coverage varies, and oral drugs may have broader formulary acceptance.
By answering these questions, you can avoid over‑paying for a product that doesn’t add clinical value.
Pros and Cons of Each Option
| Product | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| ZyhCG | Lower per‑IU cost in Australia/NZ; backed by TGA quality standards; flexible dosing for weight‑loss protocols. | Limited availability outside ANZ; requires injection; not FDA‑approved in the US. |
| Pregnyl | Widely available worldwide; higher concentration reduces injection volume. | Slightly higher price; may cause more injection‑site discomfort. |
| Novarel | Formulated for IVF, so many fertility clinics already stock it. | Higher cost per IU; less data on weight‑loss use. |
| Ovidrel | Recombinant purity reduces risk of immune response; pre‑filled syringes simplify administration. | Most expensive HCG option; dose is fixed, limiting titration. |
| Clomiphene (Clomid) | Oral, inexpensive, no injections needed. | Potential for multiple‑follicle ovulation, increasing twins risk; not effective for weight‑loss. |
| Letrozole | Effective for ovulation with lower multiple‑pregnancy rate than Clomid. | Off‑label for fertility; requires careful dosing. |
| Metformin | Improves insulin sensitivity, helps weight loss in PCOS, generally well‑tolerated. | Gastrointestinal side effects common; not a direct ovulation trigger. |
Practical Tips for Safe Use
- Always obtain a prescription and follow a physician‑approved protocol.
- Reconstitute the vial with sterile water as directed; discard any unused solution after 28days.
- Monitor serum HCG levels after the first week to confirm absorption.
- Combine HCG injections with a calorie‑controlled diet (≈1,200kcal/day) and moderate exercise to maximize fat loss.
- Report side‑effects such as headache, mood swings, or injection‑site redness immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ZyhCG approved for weight loss?
In Australia and NewZealand, ZyhCG is registered for both weight‑loss adjunct therapy and luteal‑phase support. In the United States it is not FDA‑approved for weight loss, so it can only be used off‑label under a physician’s supervision.
How does the cost of ZyhCG compare to Pregnyl?
At the current 2025 wholesale rates, ZyhCG costs about US$0.08 per IU, while Pregnyl averages US$0.10 per IU. The difference widens when you factor in shipping to the US, where Pregnyl must be imported.
Can I switch from ZyhCG to an oral alternative mid‑cycle?
Switching is possible but requires a washout period of at least 10days to avoid overlapping hormonal effects. Your doctor should recalibrate dosing based on serum hormone levels before introducing an oral agent.
What are the most common side effects of HCG injections?
Mild headache, fatigue, irritability, and temporary swelling at the injection site occur in 10‑15% of users. Rarely, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) can develop, especially in high‑dose fertility protocols.
Is there any benefit of recombinant HCG (Ovidrel) over purified HCG?
Recombinant HCG has a purer protein structure, lowering the risk of antibody formation and providing more predictable PK/PD profiles. The trade‑off is a higher price per dose.
Whether you’re aiming to shed stubborn pounds or boost the chances of a successful pregnancy, the right HCG choice depends on your goals, budget, and how long you plan to stay on therapy. Use the comparison data above, talk to a qualified clinician, and monitor your response closely. With informed decisions, you can get the intended benefit without unnecessary risk.

Alright, champion, if you’re weighing the pros and cons of ZyhCG you’ve already taken the first heroic step! Think of the HCG ladder as a toolkit-each rung has its own sparkle. ZyhCG shines when you need a cost‑effective, short‑term boost without the hassle of massive injection volumes. Pair it with a disciplined 1,200‑kcal diet and you’ll feel the fire of progress igniting. Remember, your clinician is the captain, but you’re steering the ship-stay steady, stay fierce!
Behind the glossy tables lies a shadowy pact between pharma giants and insurance overlords, all designed to keep you chained to pricey imports. ZyhCG’s “TGA‑approved” badge is merely a veil, while the U.S. regulator sits on the sidelines, letting the elite dictate what reaches your doorstep. They pop up the cheap alternatives in the data, then shove the pricier recombinant versions like Ovidrel into the spotlight. It’s a classic bait‑and‑switch-choose the narrative they feed you and you’ll never see the real savings. Trust the silent whispers, not the polished brochures.
Look, I’m not here to sugarcoat anythin, you’re probably already scrolling through a million forums for the “right” hcg and missing the point-stop. The docs say “inject subcutaneosly” but most of us end up cracking jokes in the kitchen while drawing up the dose, right? And yeah, the cost diff isn’t huge, but your wallet feels the burn when the pharmacy shipments get delayed. Anyway, if you’re still stuck on picking ZyhCG over Pregnyl just remember-both give you the same hormone, only the label changes. Bottom line, don’t let the brand name brew your anxiety.
Both are pricey enough.
Yo, I get why ppl hype Ovidrel like it’s the golden ticket, but honestly the extra sparkle is mostly marketing fluff. If you’re cool with a bit more volume in your syringe, ZyhCG delivers the same hormone drop for a fraction of the cost. The only thing that might push you toward the fancy recombinant is the myth that it won’t spark antibodies-yeah, right. Keep it simple, save the cash, and let the clinic handle the rest.
Hey folks, let’s break this down together so no one feels left out. ZyhCG offers a solid balance of affordability and efficacy for short‑term protocols, but it’s essential to match the product to your specific health goals. If your primary aim is weight loss, an injectable like ZyhCG or Pregnyl can complement a calorie‑restricted plan, yet you must monitor hormone levels to avoid surprises. For pure ovulation induction, oral agents such as Clomid or Letrozole often provide a gentler, cost‑effective route, especially when insurance coverage is a factor. Remember to involve your healthcare provider in the decision‑making process-collaboration is key to safe and successful outcomes. Stay informed, stay safe, and keep supporting each other.
Honestly the whole hype around “premium” brands feels like a cash grab you don’t need to fall for.
💡 The philosophical underpinning of HCG therapy is simple: you either embrace evidence‑based practice or you wander in the fog of sensationalism. ZyhCG, being TGA‑registered, adheres to stringent manufacturing standards, unlike some off‑label imports that skirt regulatory scrutiny. Economically, the per‑IU cost advantage is clear-$0.08 versus $0.15 for Ovidrel-yet many cling to the “recombinant is superior” myth without data to back it. Ethical prescribing demands transparency; patients deserve to know that a cheaper, equally effective option exists. 🧠 Align your treatment choice with rational cost‑benefit analysis, not with the allure of brand prestige.
It’s no coincidence that the U.S. FDA keeps a tight grip on HCG products while overseas markets like Australia and New Zealand freely distribute ZyhCG. This double standard is a strategic move to keep American dollars flowing to domestic pharma behemoths, forcing us to pay premium prices for the same hormone. The narrative that “recombinant” is magically better is just a smoke screen to justify those inflated costs. We should demand equal access, not be fooled by bureaucratic gatekeepers. Patriotism means protecting our wallets from corporate exploitation.
Upon meticulous examination of the comparative data presented, one must acknowledge the superficial breadth yet lament the paucity of rigorous, peer‑reviewed clinical outcomes. The cost analysis, while informative, fails to incorporate longitudinal efficacy metrics essential for a comprehensive assessment. Moreover, the discussion of side‑effects omits a nuanced exploration of incidence rates across diverse patient populations. Consequently, the exposition, albeit well‑structured, remains constrained by its reliance on anecdotal evidence. A more robust scholarly approach would ameliorate these deficiencies.
Think of the HCG market as a microcosm of power dynamics-those who control the narrative dictate the price tags we accept. The glorification of Ovidrel as the “gold standard” is less about science and more about national industry dominance. While ZyhCG offers comparable biochemical activity, its under‑recognition is a symptom of geopolitical bias. If we champion autonomy in medical choices, we must also challenge the monopolistic structures that inflate costs for the sake of profit. Let’s rally for transparent, evidence‑driven selections that honor both health and fiscal responsibility.